July 2024 Update - Feature Deep Dive
Generated with AI ∙ 16 July 2024 at 11:02 PM
The Oracle Analytics Cloud July 2024 update is on its way out to the general public as this blog is being written. We will focus our attention on one of the new features that significantly improves the benefits of dataset in the Oracle Analytics data visualisation tool.
You can watch this YouTube playlist below to find out details of some of the main features in the July 2024 update. For more information on the update, click here to get a comprehensive list of the features that are included in the July 2024 update.
In this blog, we'll focus on the data caching feature improvements which are part of the July 2024 update. Caching the data in datasets provides a number of benefits which include the potential for improved query performance. Being able to apply changes made to the source data has been possible previously by doing a full reload of the dataset. This can be a long drawn out process if the underlying data source has a large volume of data.
In the July 2024 Oracle Analytics Cloud update, it is now possible to incrementally update datasets. There is now the capability to only insert new rows and updates to apply any changes to existing data. which will be much better than a full data reload. This improves the data load time as well as the execution of queries against the dataset. These performance improvements that caching provides come with a downside. If you require real time data, caching is not the option for you. If intraday data changes aren't critical to your business area that you are analysing, then data caching will work for you. Business Benefits Incrementally loading data into a dataset in Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) offers several business benefits: Reduced System Load and Improved Performance: By only loading new or changed records, the system avoids reprocessing the entire dataset. This reduces the overall load on the system, leading to better performance and quicker data refresh times. Minimised Downtime: Incremental loading can be scheduled during off-peak hours or more frequently, ensuring that the system is always up-to-date without significant downtime or disruption to users. Faster Data Refresh: Since only new or updated data is processed, the time required to refresh datasets is significantly reduced. This allows for more timely and accurate data availability for business analysis and decision-making. Scalability: Businesses can scale their data operations more effectively with incremental loading, handling larger datasets without the need for massive resource increases. This supports business growth and the integration of more data sources. Enhanced Data Accuracy and Relevance: With more frequent and efficient data updates, businesses can ensure that their analytics are based on the most current data. This leads to more accurate insights and better-informed decision-making. Improved User Experience: End users experience faster query responses and up-to-date data, which enhances their ability to perform timely and effective analysis. This leads to higher user satisfaction and greater adoption of the analytics platform.
Implementing incremental data loading in Oracle Analytics Cloud supports these benefits, enabling businesses to maintain efficient, scalable, and cost-effective data management practices. Data caching is not available to all data sources. You can get a full list of supported data sources from here.
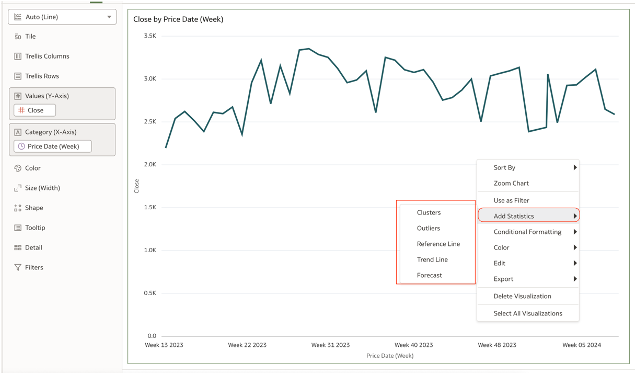
There are 2 methods that can be used to set the incremental dataset cache refresh; this can be done either in a visualisation or directly within the dataset itself. Configuration in a Visualisation The image below shows you how to set this up in a visualisation.
Change the Data Access from Live to Automatic Caching and then change the Cache Reload Type to Load New and Updated Data.
Configuration in a Dataset
The image below shows how the incremental caching is set up in a dataset.
As described above, you can set up a variety of data sources to refresh incrementally and these can be run manually as above. If there is a requirement for the dataset to be regularly refreshed then a schedule can be set up to enable this. Below, you can see how to set up a schedule that can be used to automate the cache refresh of the dataset. You can also view the details of the schedule and detail of the schedule executions.
Incremental data loading of datasets in Oracle Analytics Cloud offers significant business benefits by enhancing system performance and efficiency. By only loading new or updated records, it reduces system load, minimizes downtime, and accelerates data refresh times. This approach optimises resource utilisation, providing cost savings and enabling scalability for larger datasets. Additionally, it ensures data accuracy and relevance, improving the user experience with faster query responses and up-to-date information.
Overall, incremental loading supports efficient, scalable, and cost-effective data management practices, crucial for informed decision-making and business growth.
0 Comments
The Future of Data Exploration: Oracle Database 23ai's Features Empower Oracle Analytics Cloud3/5/2024 Oracle recently made the latest version of their database: Oracle Database 23ai generally available, the next generation of its database incorporates a number of AI capabilities. There are over 300 new features in this new release and we'll be looking at some of these features from an Analytics perspective, empowering you to unlock deeper insights from your data. Some of the highlights of the Oracle Database 23ai release are discussed in this video below.  Converged Database Oracle Database 23ai is a Converged database which means that a single database can be used to store data in relational, graph, vector, spatial, JSON and several other formats. Here's how a converged database facilitates this: Unified Data Access: By storing and managing diverse data types within a single database system, a converged database eliminates the need for separate data silos and specialised databases for different workloads. This unified data access makes it easier to query, analyse, and generate insights across multiple data types without the overhead of complex data integration or movement between different systems. Consistent Data Governance: With all corporate data workloads stored in a converged database, it becomes easier to implement consistent data governance policies, security controls, and access management across the entire data landscape. This ensures data integrity, compliance, and proper access controls when generating insights from various workloads. Cross-Workload Analysis: A converged database allows you to perform cross-workload analysis by combining data from different sources and types. For example, you could analyse spatial data in the context of relational data, or enrich graph data with information from blockchain workloads. This cross-pollination of data can lead to more comprehensive and valuable insights. Unified Query Processing: By having a single query processing engine that can handle diverse data types, a converged database can optimise query execution and leverage advanced techniques like vectorisation, parallelisation, and indexing across different workloads. This can lead to faster and more efficient insight generation, especially for complex queries spanning multiple data types. Simplified Data Pipelines: Instead of maintaining separate data pipelines and ETL processes for each workload, a converged database allows you to streamline data ingestion, transformation, and analysis workflows, reducing complexity and potential sources of error. Improved Collaboration: With all corporate data workloads residing in a single converged database, it becomes easier for different teams and departments within an organisation to collaborate, share data, and generate insights collectively. This can foster better cross-functional analysis and decision-making. Future-Proofing: As new data types and workloads emerge, a converged database architecture can more easily adapt and incorporate them, future-proofing your data infrastructure and reducing the need for frequent migrations or replacements of specialised databases. AI Vector Search is another feature that can improve insights derived from your corporate data as it provides the functionality to access data in all the formats allowing foundation models like OpenAI's ChatGPT, Microsoft's Copilot, Anthropic's Claude to name a few to provide more accurate responses with access to all data in the Oracle Database 23ai. 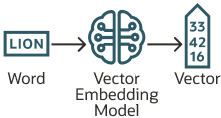 AI Vector Search Another noteworthy feature introduced in Oracle Database 23ai is AI Vector Search. This functionality has the potential to significantly improve how users gain insights from their data. Unlike traditional keyword searches, AI Vector Search goes beyond simply matching terms. Instead, it focuses on understanding the underlying meaning and relationships within your data. This is achieved by converting text, images, and even relational data into mathematical representations that capture their essence. By comparing these representations, the database can identify information that aligns most closely with your query, regardless of its format or specific wording. This more semantic approach to searching unlocks new possibilities for data exploration within Oracle Analytics Cloud. Users can uncover previously hidden connections and patterns within their data, leading to a richer understanding and the ability to make more informed decisions. AI Vector Search is considered a significant benefit of a converged database when it comes to improving generated insights across a wide range of corporate workloads, including relational, spatial, graph, and blockchain workloads. Here's how AI Vector Search can enhance insight generation in a converged database environment: Unified Data Representation: By representing diverse data types as vectors, AI Vector Search allows for a consistent and unified representation of data across different workloads. This enables the application of machine learning and AI techniques consistently, regardless of the underlying data structure or format. Semantic Search: AI Vector Search leverages the power of vector representations to capture the semantic relationships between data elements. This enables more meaningful and context-aware searches, leading to better insights by retrieving relevant information based on conceptual similarity rather than just exact matches. Cross-Workload Similarity Analysis: With vector representations, AI Vector Search can identify similarities and patterns across different workloads, even if the data types are distinct. For example, it could uncover relationships between spatial data and graph data, or find connections between blockchain transactions and relational data, enabling novel insights and discoveries. Improved Query Performance: AI Vector Search typically uses specialised indexing techniques optimised for vector data, enabling faster and more efficient querying across large datasets spanning multiple workloads. This can significantly accelerate the process of generating insights, especially for complex analytical queries. Scalability: AI Vector Search can scale more efficiently than traditional search methods, as vector representations are typically more compact and can leverage techniques like dimensionality reduction. This scalability is crucial when dealing with the ever-increasing volumes of data across diverse corporate workloads. Integration with AI/ML Models: The vector representations used in AI Vector Search are compatible with many AI and machine learning models, enabling seamless integration of these advanced techniques for enhancing insight generation. For example, natural language processing models could be used to query and analyse text data across different workloads. I'd strongly recommend spending a bit of time taking this LiveLabs workshop to get an understanding of the vector data type basic principles.
Here's a breakdown of the steps to configure this setup: 1. Setting Up SharePoint Permissions:
By leveraging the AI Vector Search feature, the company can gain deeper and more nuanced insights from their data, leading to better-informed business decisions and a more responsive approach to customer feedback However, it's important to note that realising the full benefits of a converged database for generating insights across diverse workloads may require careful data modelling, performance optimisations, and leveraging the advanced analytical capabilities provided by the database system, such as machine learning, graph analytics, and spatial analysis functions. Conclusion
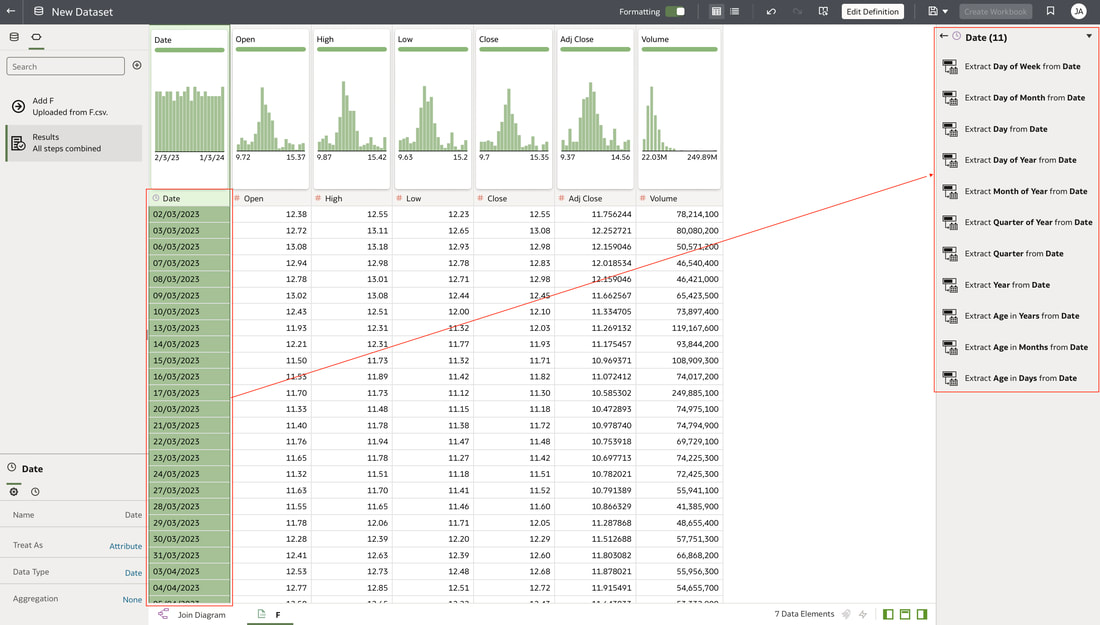
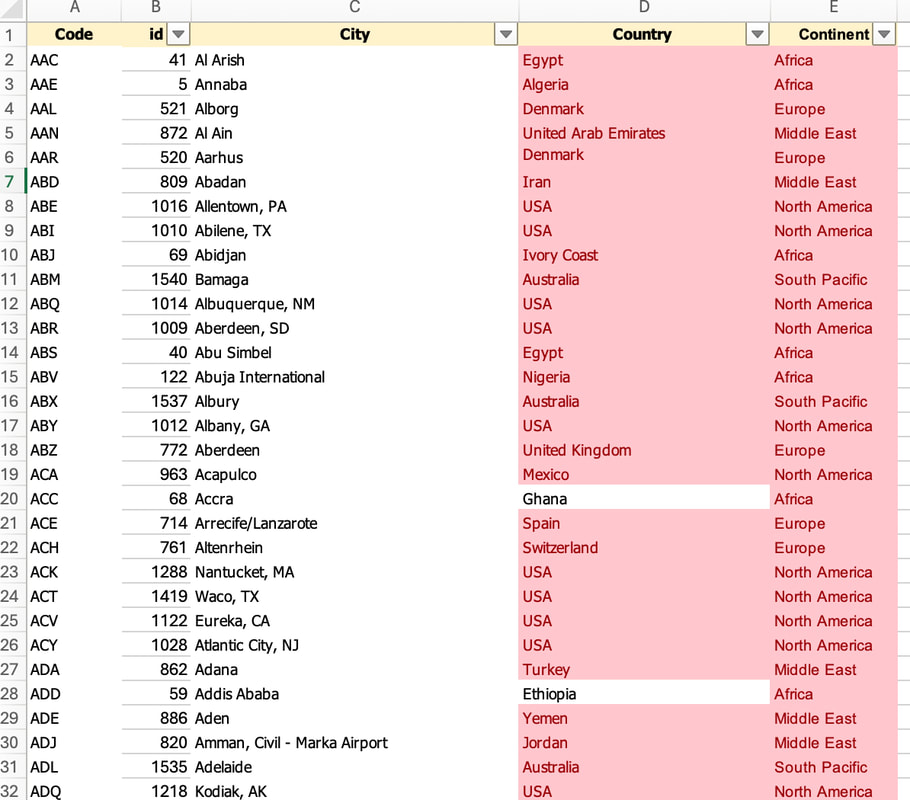
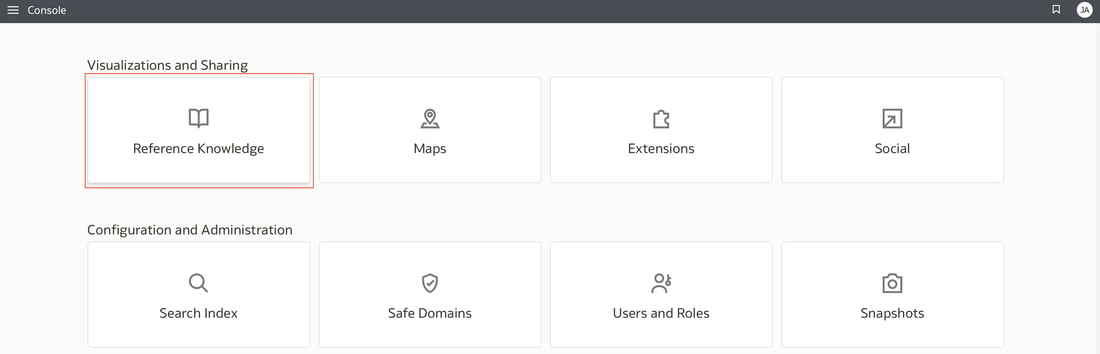
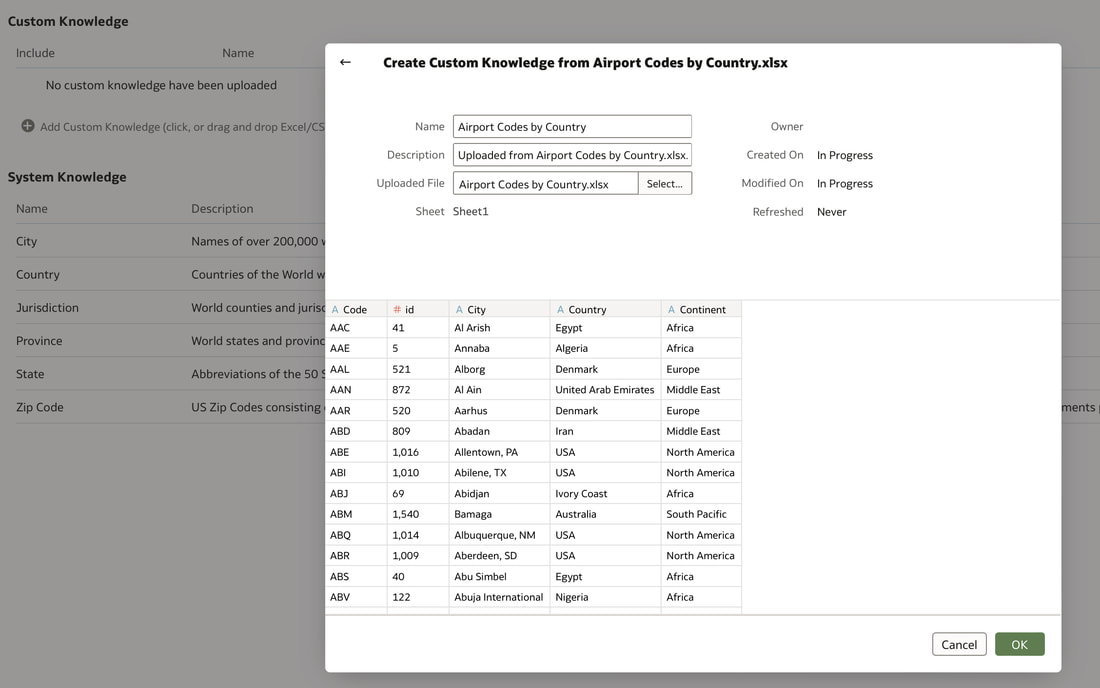
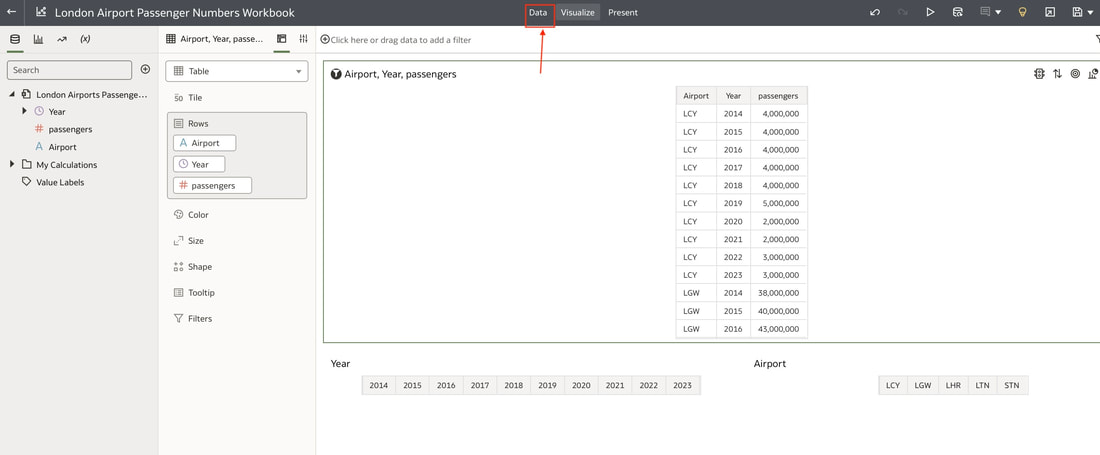
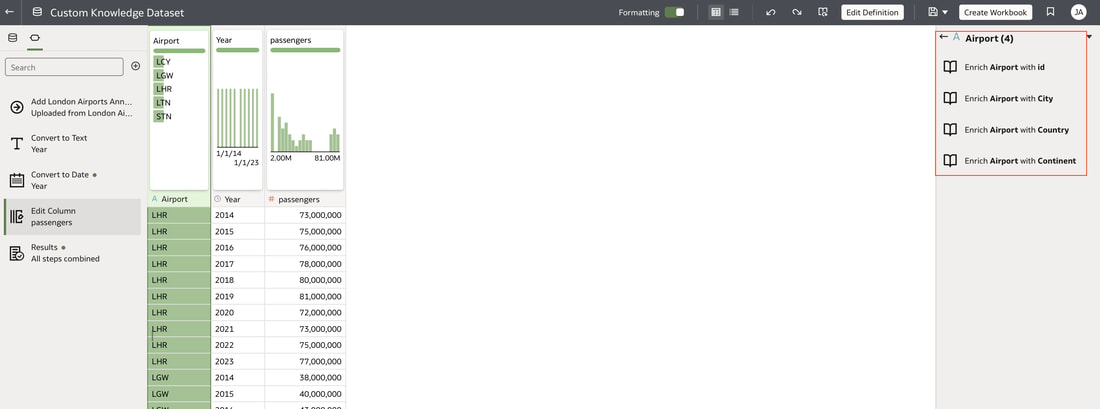
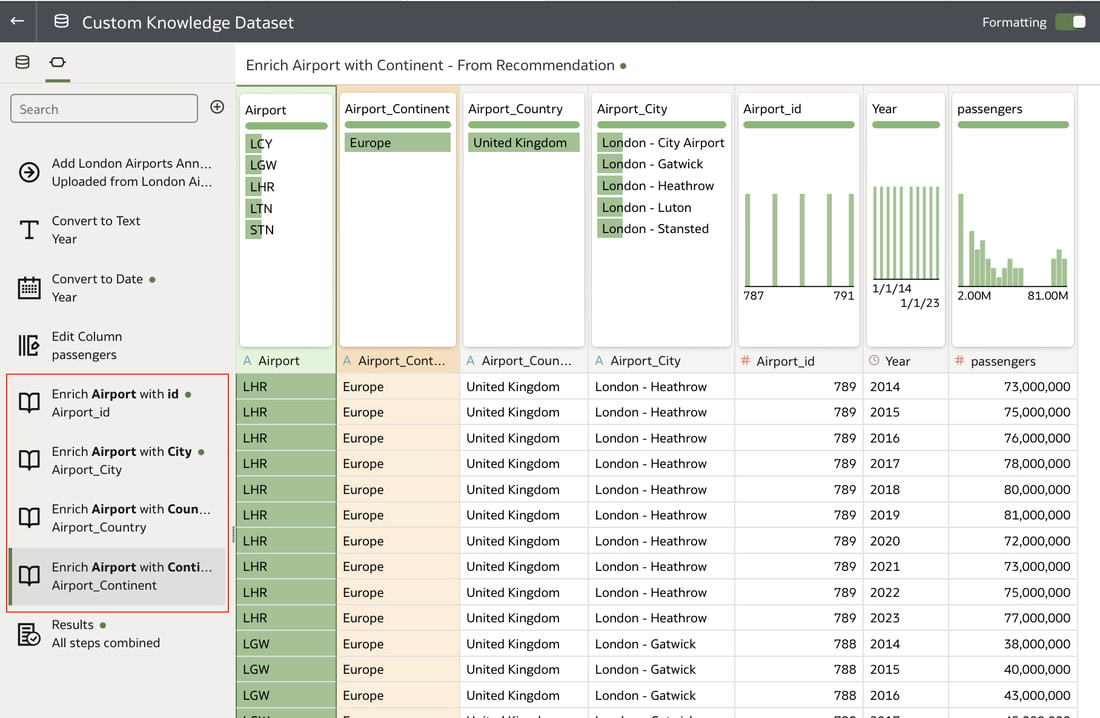
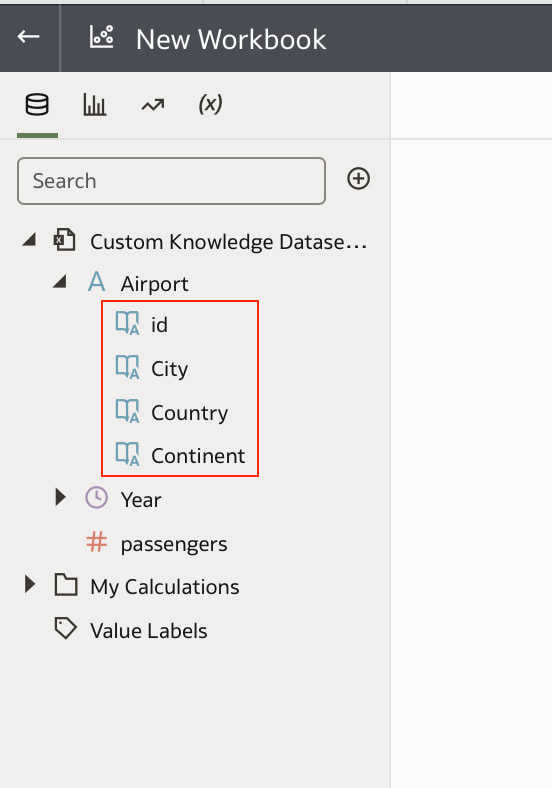
In conclusion, Oracle Database 23ai with its converged database architecture and AI Vector Search has the potential to unlock a new level of data exploration within Oracle Analytics Cloud. By storing all your corporate data, structured and unstructured, in a single platform, you can leverage the power of AI to search for insights across different data types using natural language. This not only simplifies data exploration and data integration for users but also empowers them to uncover hidden connections and patterns that might be missed with traditional keyword searches. As a result, Oracle Database 23ai paves the way for a more intuitive and insightful data analysis experience within Oracle Analytics Cloud, ultimately leading to better data-driven decision making. When you create a dataset in Oracle Analytics, the system performs column-level profiling to generate semantic recommendations for data enrichment. Additionally, when creating workbooks, you can enhance visualisations by including knowledge enrichments from the Data Panel. These recommendations are based on automatic detection of specific semantic types during the profiling process. Semantic types include geographic locations identified by city names, recognisable patterns (such as credit card numbers, email addresses, and social security numbers), dates, and recurring patterns. In the share price dataset below which has a date column selected, the panel on the right hand side provides semantic recommendations related to the date column which can be added to the dataset to provide additional classifications in addition to the original date from the data set like the month, quarter and year. This is very helpful in adding new ways to look at data but this is limited to the system built-in semantic recommendations that come with the Oracle Analytics platform. Most companies have domain specific knowledge which would be useful in this context to provide enrichment possibilities to users. In the sample file below which contains geographic information about airport codes, this can be used to give additional geographic context to datasets that only contain the 3-digit airport code. To demonstrate this feature, we will be adding some custom knowledge that can be used to enrich 3-digit airport codes with additional information about the airport name, country and continent. As an Administrator, click the Reference Knowledge button in the Oracle Analytics administration console. Click on "Add Custom Knowledge". 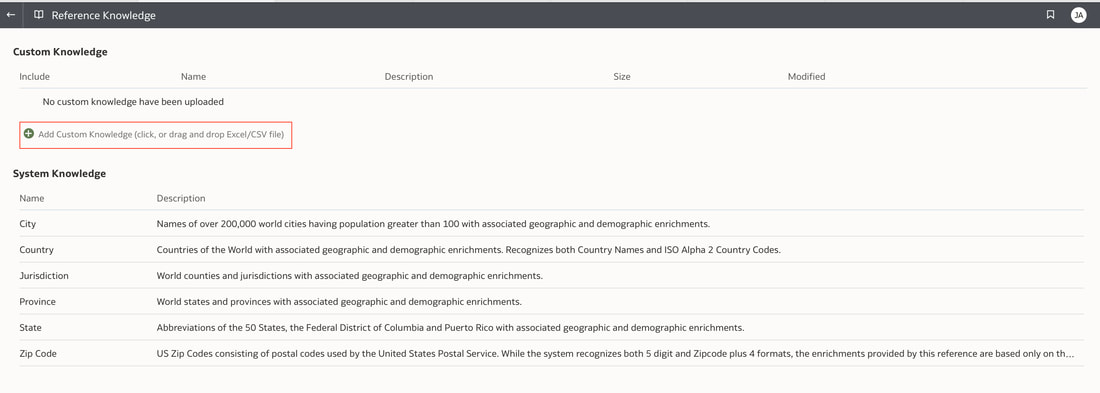 Select the file (either an XSLX or CSV format) with the custom knowledge to upload. I have noticed that the first column in the data to be uploaded to custom knowledge should be the unique key used to identify each record uniquely. In the case above, the 3-digit airport code is unique and should be the first column in the data. Review the content in the window below and click OK if all looks good. Now that the custom knowledge has been uploaded to Oracle Analytics, it is now available to be used in workbooks that have the airport code in their datasets. This workbook has a list of London airports and their approximate passenger numbers form 2014 - 2023. We can make use of the custom knowledge to enrich this workbook. Navigate to the Data tab and you should now see recommendations for the Airport column with options as seen in the screenshot below. The enrichments can be seen here and will now be available to use within the workbook. Alternatively, the enrichments can also be seen directly in the workbook data panel enabling non-administrator users to have access to these enrichments. What would improve this feature would be having an option to derive the custom knowledge from a database source for the purposes of data governance. A refresh schedule would be a welcome addition to the feature as well ensuring that the custom knowledge is sourced directly from a database but also routinely refreshed to ensure that the custom knowledge is kept up to date.
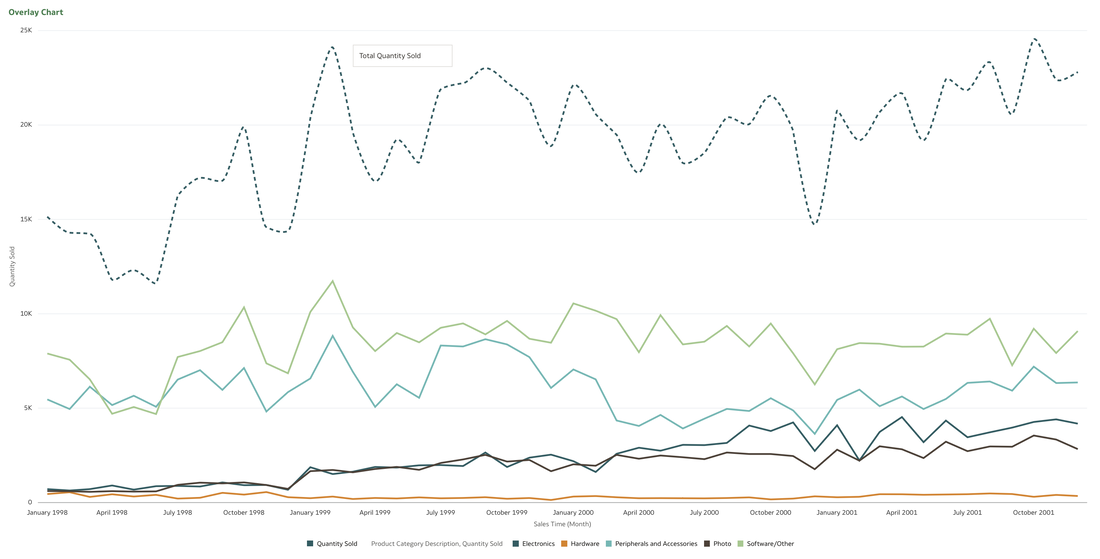
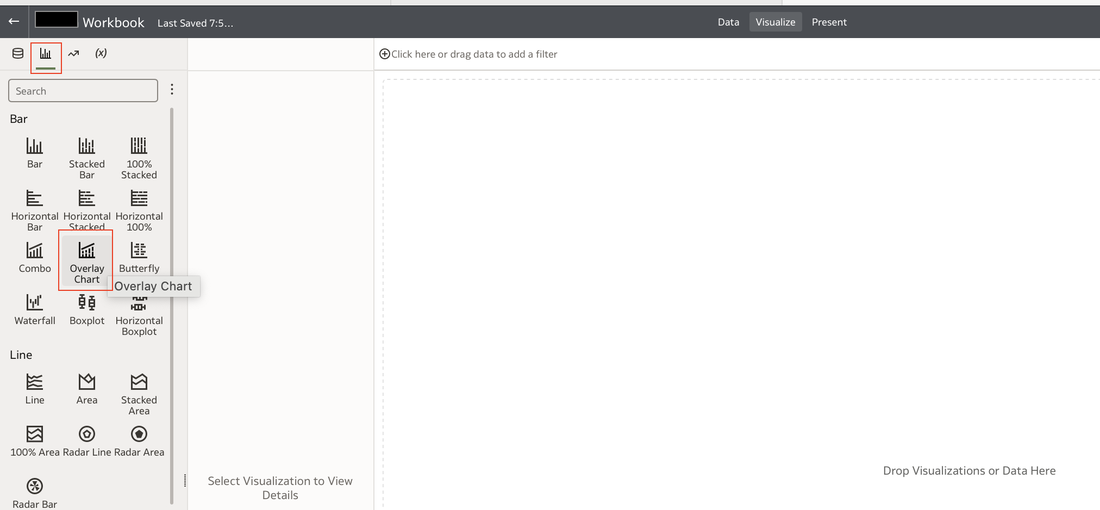
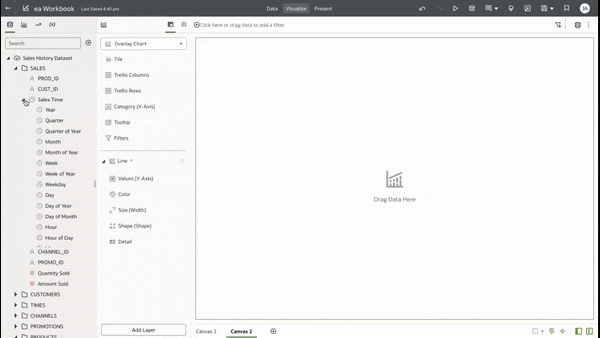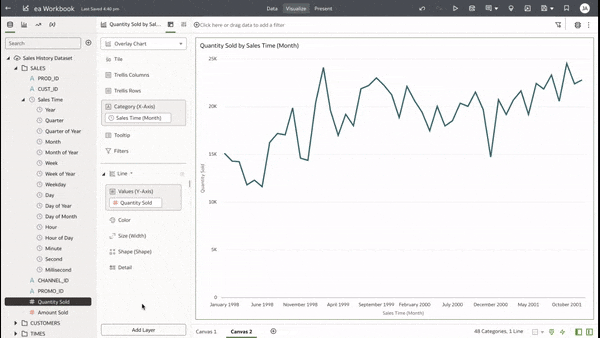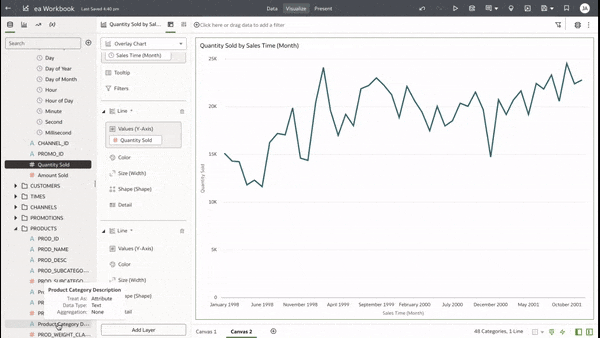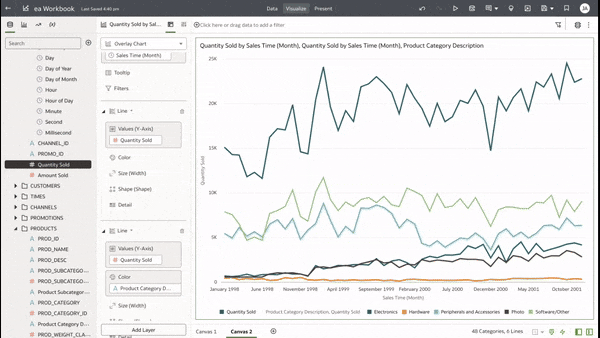
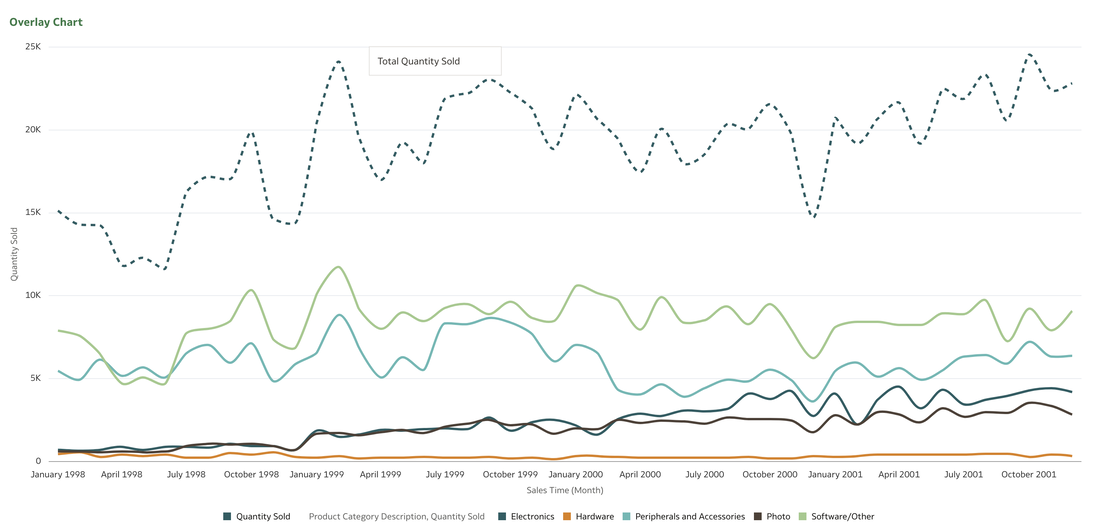
This functionality serves as a valuable tool that can empower users to achieve a deeper understanding of their data and extracting insights that have greater relevance to the end user. In data visualisation, it's often desirable to present both high-level summaries and detailed breakdowns within the same view. This enables users to have a view of the bigger picture while still having access to the underlying granular data points. This seamless integration can be challenging, especially when working with disparate data sources or attempting to convey complex relationships. Fortunately, Oracle Analytics Cloud offers a powerful charting feature known as the overlay chart, which elegantly solves this problem. By combining multiple chart types into a single visualisation, the overlay chart enables you to layer summary-level metrics on top of more detailed visualisations, providing a comprehensive and cohesive view of your data. In the data panel, select the visualisations tab and then select the Overlay Chart. Double click or drag it into the visualise canvas. For the first layer, add the quantity sold measure to the Y axis and the Time dimension month attribute to the X axis. For the second layer, repeat the above and add the Product Category Description to the colour section. The overlay chart is a powerful data visualisation tool in Oracle Analytics Cloud that enables seamless integration of high-level metrics and granular details within a single view. By layering multiple chart types, you can construct rich, multifaceted data stories. Whether unveiling executive summaries backed by granular evidence or pinpointing critical operational insights amidst a sea of data, the overlay chart empowers you to communicate with clarity and impact. As you continue to explore the capabilities of this versatile charting technique, you'll unlock new avenues for data-driven storytelling, fostering a deeper understanding of your business landscape and driving more informed decision-making across your organisation. Embrace the overlay chart, and elevate your ability to transform raw data into compelling narratives that inspire action and drive meaningful change.
In the data-driven world we live in today, the ability to extract insights from vast and complex datasets is paramount for organisations to make informed decisions, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge. With the exponential growth of digital information, estimated to reach a staggering 44 zettabytes (roughly a billion terabytes) in 2020 according to the World Economic Forum, businesses are grappling with the challenge of navigating this vast amount of data. This is where powerful analytics platforms like Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) come into play, harnessing the transformative capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Authoritative Industry Projections Highlighting Rapid AI Software Growth and Enterprise Adoption According to a number of the leading global research and advisory firms, there is a shared opinion that forecasts the rapid growth and widespread adoption of AI software, solutions, and generative AI capabilities across enterprises globally, driven by the potential benefits and competitive advantages offered by these technologies. 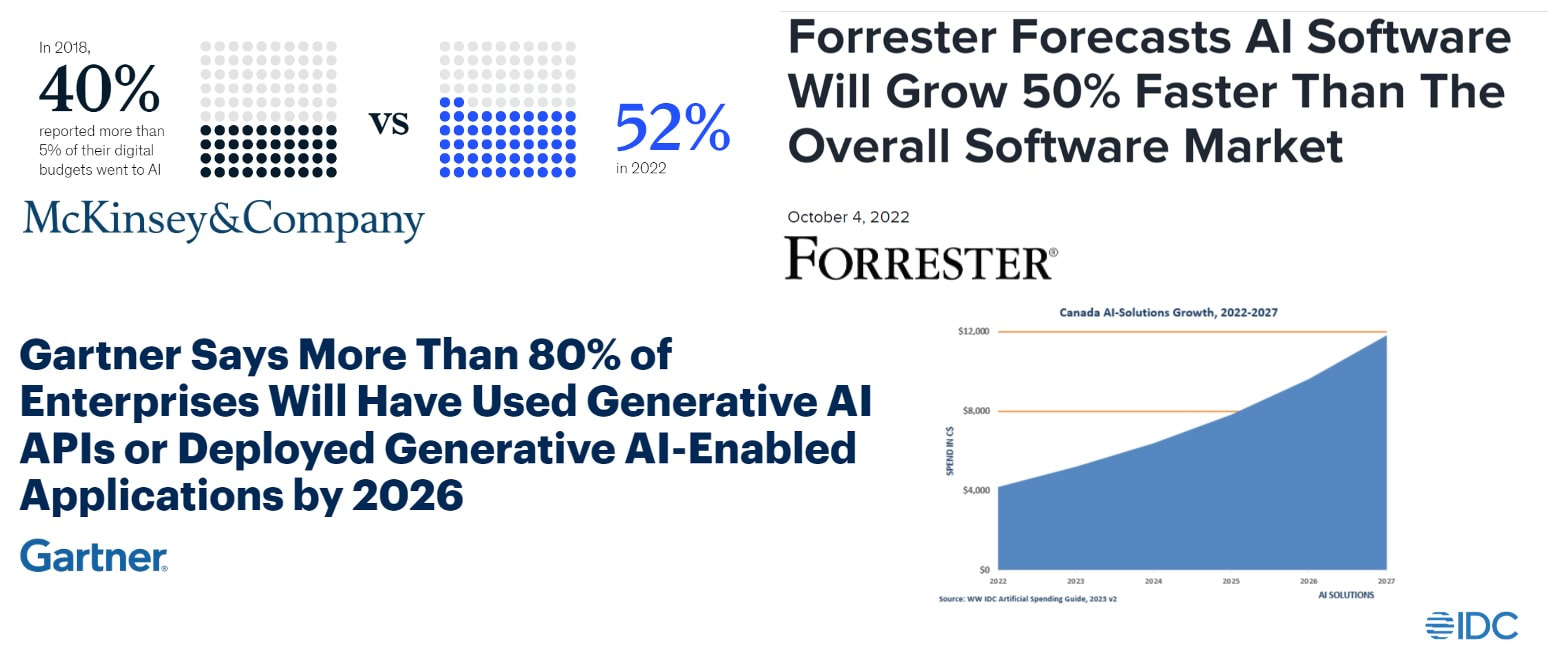 Researchers AI adoption forecasts Researchers AI adoption forecasts AI is rapidly becoming a critical technology that organisations across industries cannot afford to ignore. Those that proactively embrace AI, build the required capabilities, and integrate it into their strategies and operations will be better positioned to navigate the disruptions and capitalise on the opportunities presented by this transformative technology. Democratising Machine Learning with Oracle Analytics Cloud ‘s AI Integration At the heart of Oracle Analytics Cloud's capabilities lies the integration of AI and machine learning technologies. AI, which enables computers and digital devices to simulate human-like intelligence by learning, reasoning, and making decisions, has revolutionised various industries, from healthcare to finance. Machine learning, a subset of Artificial Intelligence is a technique that allows systems to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. Oracle Analytics Cloud leverages machine learning capabilities to empower users with a user-friendly interface for building, training, and deploying predictive models. This democratisation of machine learning empowers even non-technical users to harness the power of data-driven insights for decision-making. Key Machine Learning Features in OAC
Integrated Machine Learning Algorithms Oracle Analytics offers a set of built-in machine learning (ML) algorithms that you can leverage for various data analysis tasks. These algorithms are designed to be user-friendly and accessible through a drag-and-drop interface, eliminating the need for coding knowledge. The following algorithms are available:
You can find out more about the various OCI AI integrations currently available in Oracle Analytics Cloud.
In addition to these user-friendly features, OAC offers access to a wide range of built-in machine learning algorithms, catering to diverse analytical needs and user personas, from casual end-users to data scientists.
Benefits of AI-Powered Analytics with OAC Integrating AI and machine learning capabilities into the analytics workflow offers numerous benefits for organisations:
The Evolving Role of AI in Analytics As AI and Machine Learning technologies continue to advance, their role in the analytics domain is evolving. Traditionally, the focus has been on automating repetitive tasks and streamlining data preparation processes. However, the true power of AI lies in its ability to unlock predictive capabilities, enabling organisations to go beyond descriptive and diagnostic analytics. With AI-powered analytics platforms like OAC, businesses can leverage predictive recommendations and future trend forecasts, gaining a competitive edge by anticipating market shifts, customer preferences, and potential risks or opportunities. Upcoming Oracle Analytics Generative AI Features Oracle is at the forefront of integrating cutting-edge AI capabilities into its analytics platform. According to a forward looking statement from James Richardson's blog, here are two highly anticipated features that we might see incorporated into Oracle Analytics:
The Future of AI in Oracle Analytics Oracle's roadmap for AI integration in its analytics platform is ambitious and forward-thinking. While the first AI integrations will be "behind the scenes" to improve productivity, the ultimate goal is to augment human intelligence with AI-powered insights. Enhancements to features like Auto Insights and the AI Assistant are on the horizon, leveraging the capabilities of generative AI to provide more comprehensive and contextual insights. As AI continues to evolve, its role in analytics will shift from mere automation to true augmentation, empowering users with AI-driven recommendations, forecasts, and actionable insights. As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow exponentially, embracing AI-enabled analytics platforms like Oracle Analytics Cloud will be crucial for organisations seeking to stay competitive and data-driven. By harnessing the power of AI and machine learning, businesses can uncover actionable insights, automate tasks, and make informed decisions that drive innovation, enhance customer experiences, and ultimately fuel success in the ever-changing digital landscape. REST (REpresentational State Transfer) APIs (Application Programming Interface) are a way for software systems to communicate and share data over the internet using HTTP requests. REST APIs enable different systems to exchange data in a standardised way. Simply put, an API is a set of rules which enable different software applications to communicate with each other defining how the software applications should interact without having to know about the internal complexities of each application. This analogy further explains an API; think of an API as a waiter in a restaurant. When you (the client) want to order food which is analogous to requesting information or services, you do not need to fully understand what the Chef needs to do to get your order prepared. You, the client made your request to the waiter who acts as an intermediary (in the way that an API is the go-between) ensuring that communication between the client and the kitchen is executed and then returns the food ordered to the client. Some key aspects of REST APIs:
The January 2024 update includes an extension to the available REST API endpoints that now provide catalog management capabilities. In Oracle Analytics Cloud, REST APIs allow external applications to integrate with and extend the capabilities of OAC. Some examples of how REST APIs are used:
Mike Durran from the Oracle Analytics Product Management team has put together a video available on YouTube that walks through these endpoints. REST APIs provide a standardised way for Oracle Analytics Cloud to exchange data and interoperate with other systems. The APIs allow OAC capabilities to be leveraged from external apps and workflows. REST APIs can help enable clean handoffs between developers and production support teams for Oracle Analytics Cloud deployments, without the production support teams requiring extensive OAC expertise from the operational perspective of Oracle Analytics. Catalog Rest APIs Some of the new REST API endpoints released in the January 2024 update that now allow for catalog management. Here is a list of the new Oracle Analytics Cloud REST API endpoints:
The curl command below is an example of how one of these endpoints looks like. List Workbook Catalog Objects
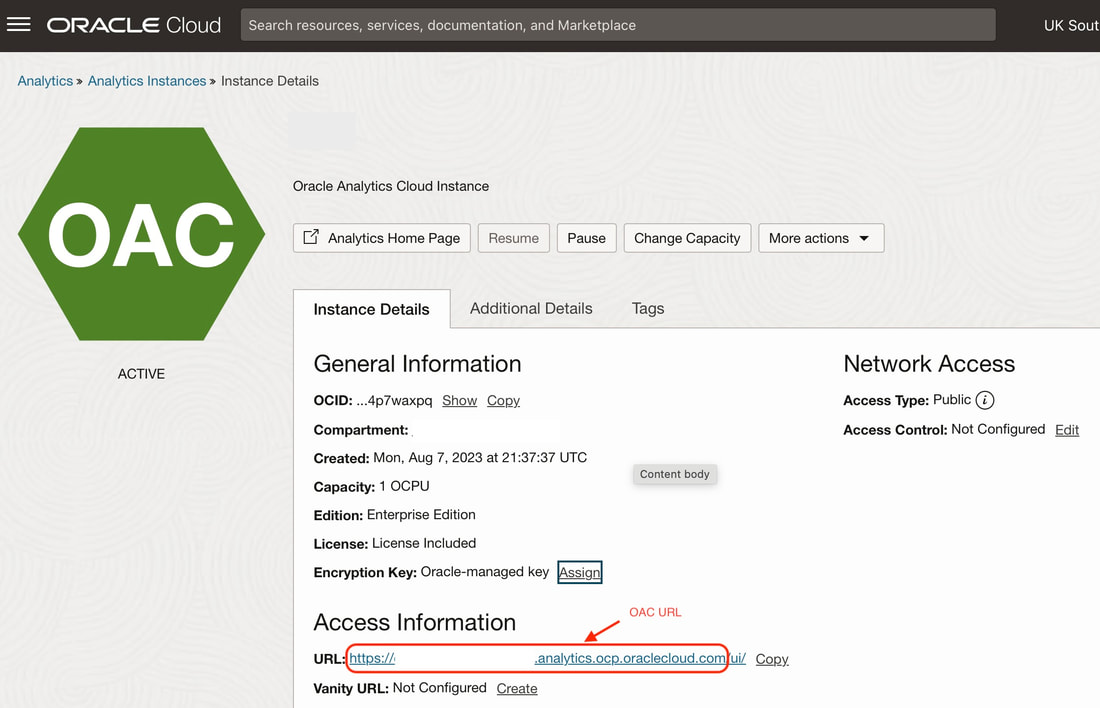
The {{OAC_URL}} portion of the URL (above) to use in the REST API endpoints can be retrieved from your Analytics Instance detail page as below: Developers can build automated deployment pipelines and operations runbooks that call OAC REST APIs to perform releases. For example, the pipeline can use APIs to validate the system health, check for availability of required roles/capacity, import metadata like dashboards or reports, and switch traffic to the new version.
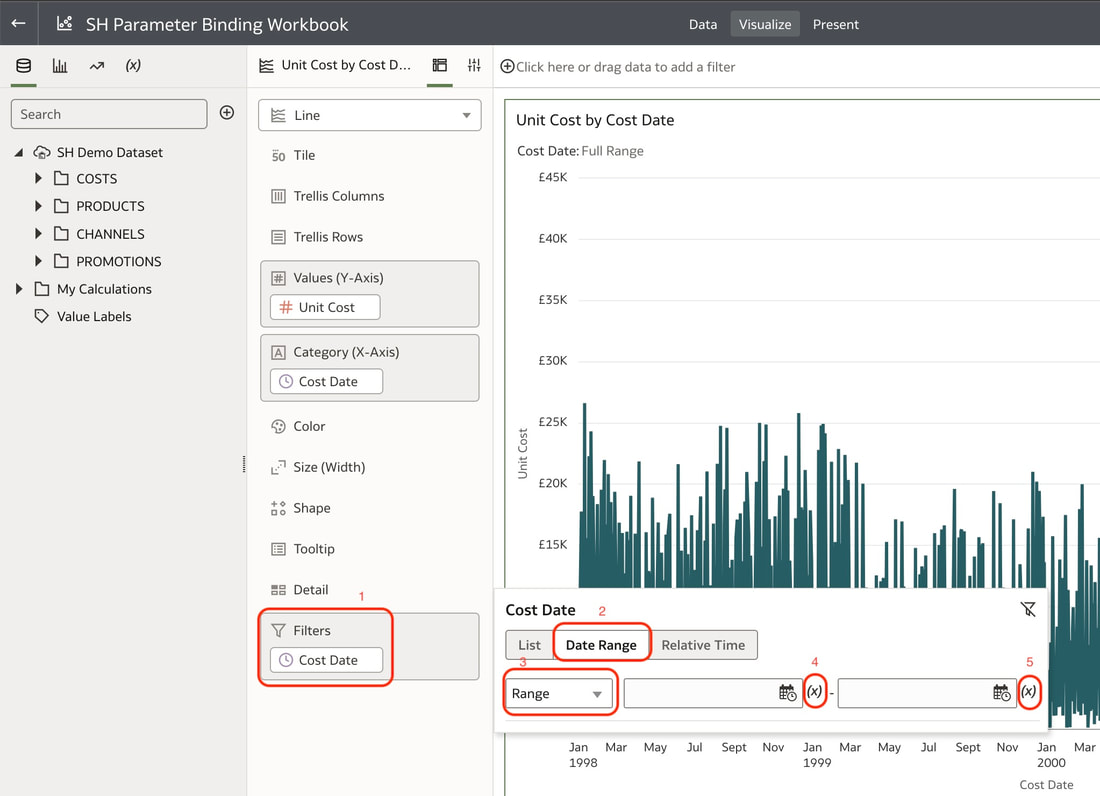
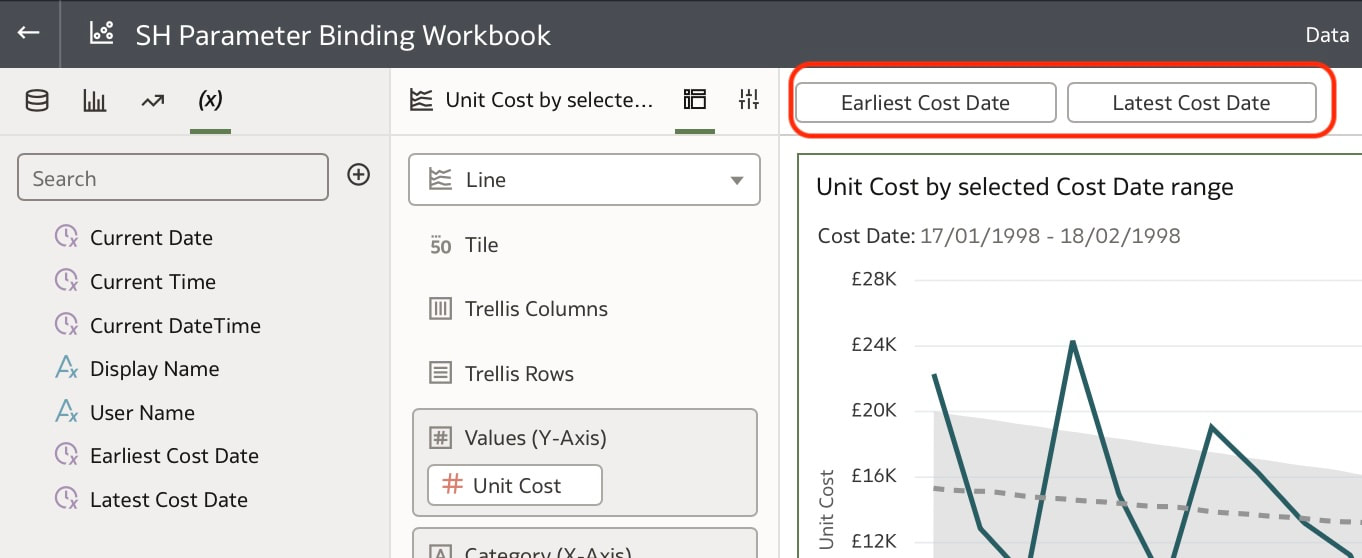
The operations team does not need deep application knowledge, just the ability to invoke APIs and monitor for errors. The actual deployment logic is encapsulated in code and triggered through API calls. This allows a clear separation of development teams from production environments - developers own building the logic and automation leveraging their OAC expertise, while operations teams focus on running and monitoring the operational aspects. The APIs serve as the interface layer between the two. This prevents fragile handoffs where operations need to learn and understand OAC internals, rely on manual processes or even rely upon the development teams to carry out these activities in production environments. Access to production can be minimised once APIs are implemented. Overall, OAC REST APIs enable easier collaboration between developers and production teams. Releases can be made reliable and repeatable through automation using APIs, reducing risks and errors caused by manual processes. The APIs abstract away the complexity and provide self-service capabilities to operations teams. The second part of this blog will dive into more technical detail on how these REST APIs are set up using an API client tool to interact with the API endpoints. We'll also look at how these REST APIs can be used by operations teams. Parameter binding in Oracle Analytics Cloud refers to the ability to bind prompt values to filter components (for example) in data visualisation workbooks. The November 2023 update includes an extension to the parameter functionality which allows you to be able to bind a parameter to a range filter in a workbook. Data Visualisation parameters in Oracle Analytics Cloud allow you to vary aspects of a visualisation at runtime using prompt selections. Some key points:
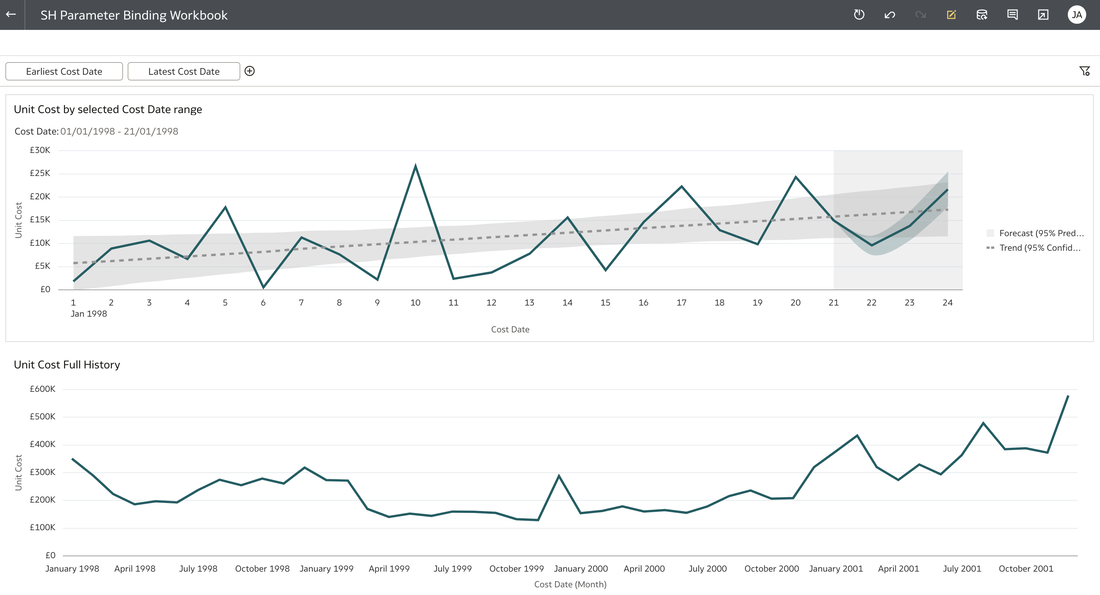
Data Visualisation parameters enhance flexibility, interactivity, and reuse by linking runtime user selections to the visualisations in an Oracle Analytics Cloud workbook. In the workbook above, a parameter has been bound to the Cost Date attribute. The filter on the visualisation at the top of this workbook was set up as a range filter on the Cost Date. In the visualisation that you would like to apply a range filter, follow the steps below:
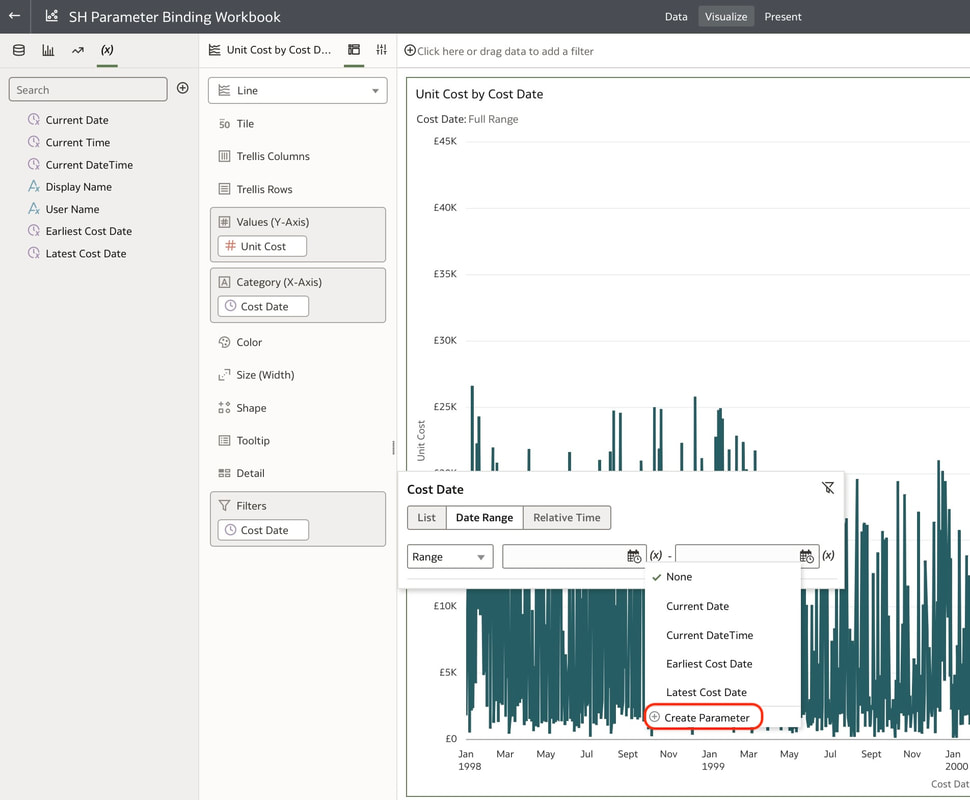
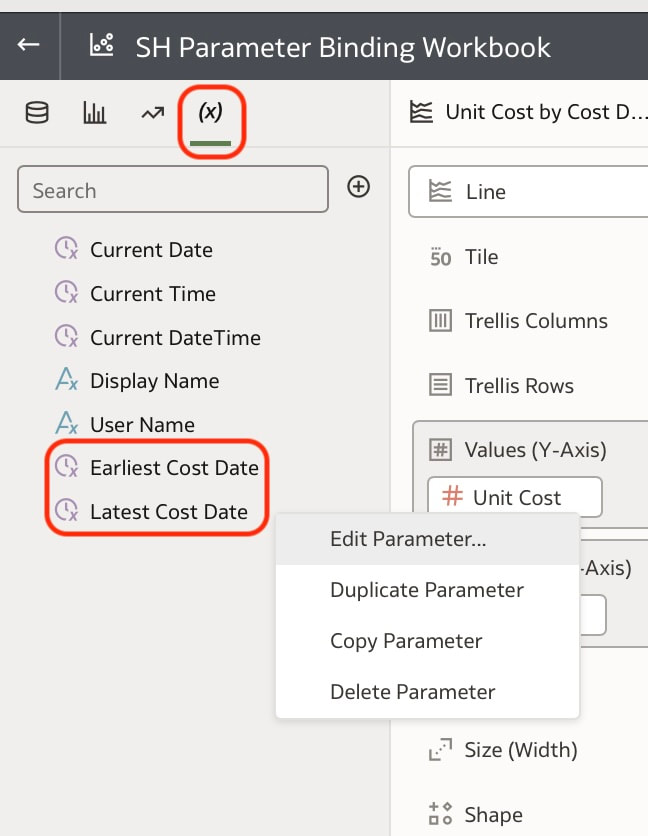
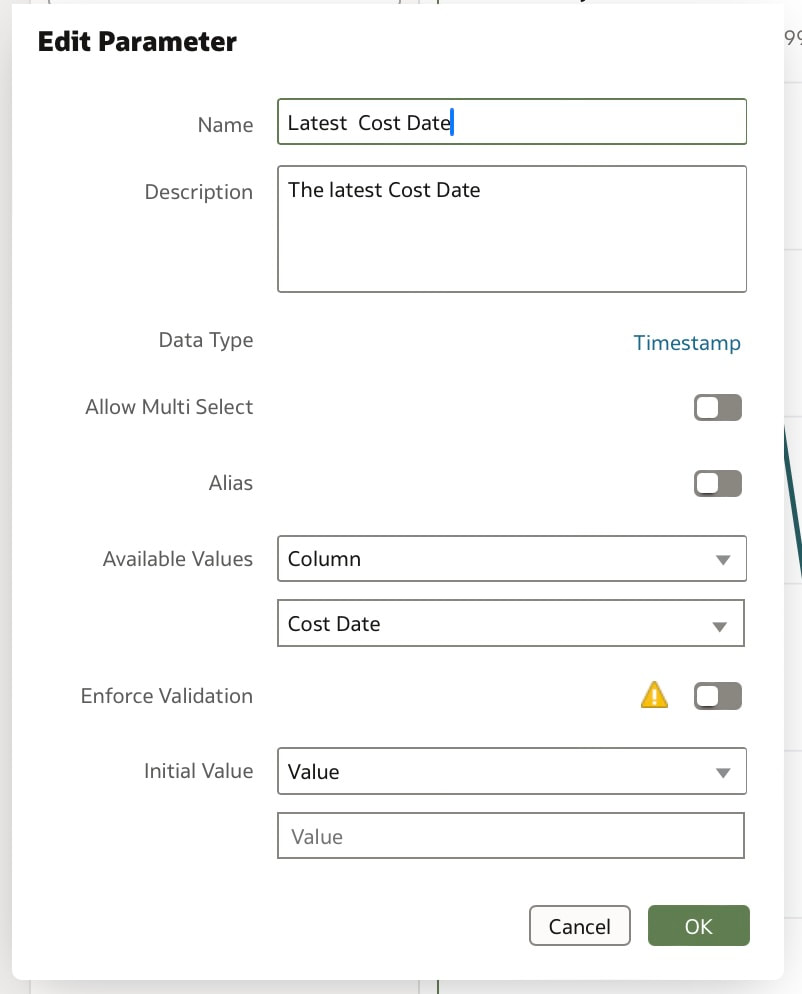
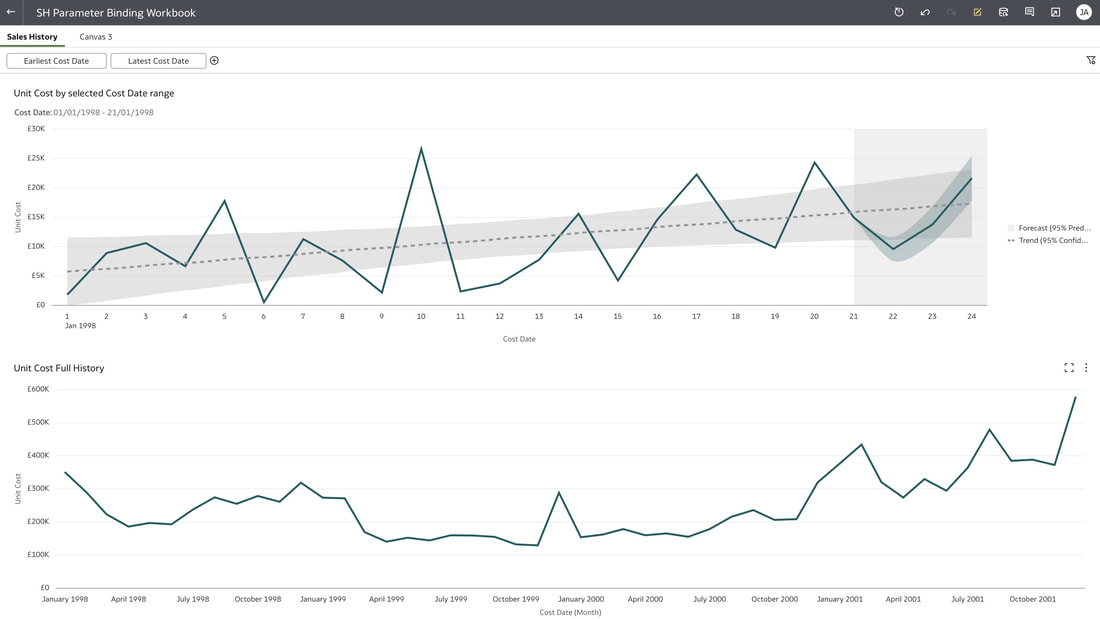
These steps create 2 parameters and binds the filter range to these parameters which you can see in the parameters tab in the Data panel. You can modify the automatically generated parameters if required by right clicking on the parameter. Useful Use Case You may have a situation where you want to show the full history on a canvas and also to show a subset of this in another visualisation. You can achieve this by creating the 2 visualisations. In the visualisation that should show the subset of data, you will need to create a range filter and bind to a parameter as we have done above. The next step would be to drag the parameters from the data panel to the filters panel This will enable you to have the visualisation with a subset of data as well as another visualisation with the full history on the same canvas. Conclusion
The new feature included in the November 2023 update that we have just looked which enables the use of parameters bound to range filters adds additional capabilities to the data visualisation parameters. Features like binding prompt values to various visualisation properties allow for adaptable, interactive visualisations that can change on the fly based on user input. Whether selecting metrics or filtering data points, parameterisation facilitates reuse of workbooks. With visualisation parameters' ability to tap into prompt user selections and feed those dynamic values into the configuration of charts, graphs, maps and more, Oracle Analytics Cloud provides an excellent toolkit for customisable, exploratory data analysis. Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) and Microsoft Power BI are two of the most popular platforms organisations use for data visualisation, reporting, and business analytics. It is common for companies today to have a "hybrid analytics ecosystem" meaning they utilise both OAC and Power BI, rather than standardising on just one. There are several reasons a hybrid approach may emerge: Oracle Analytics and Microsoft Power BI are 2 popular choices for businesses around the world for their Analytics solutions. In many cases, there is what I'll refer to as a "hybrid analytics ecosystem". Hybrid Analytics Ecosystem Many organisations today have a "hybrid analytics ecosystem" - meaning they use both Power BI and Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) or any other combination of analytics platforms for different analytics and reporting needs. There are several reasons this hybrid approach may emerge:
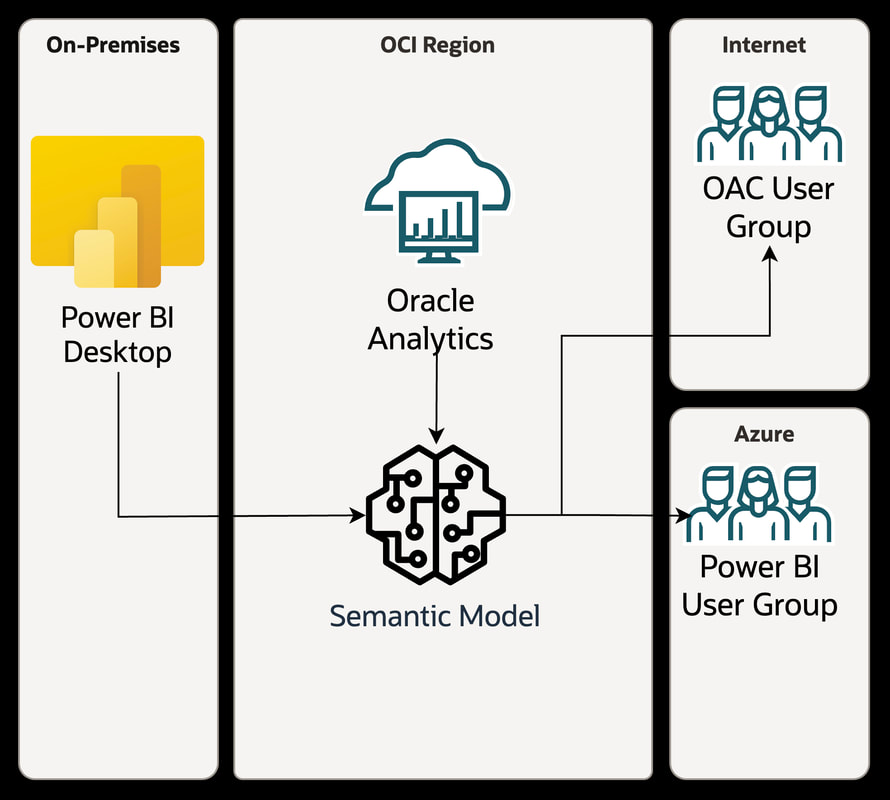
Whatever the reason, it's common for organisations to have a footprint in both Power BI and OAC (or any other combination of analytics platforms). This used to be seen as a challenge - "which one do we standardise on?" But modern integration and alignment features allow both platforms to coexist and complement each other rather than compete. This provides flexibility to leverage the strengths of both tools. The goal of this post is to show how Power BI and OAC can work together effectively in a hybrid analytics model to deliver insights across the business. Benefits of each platform An important benefit of Power BI is its tight integration with Microsoft 365 and components like Excel. Users are already familiar with Excel for ad hoc analysis, and Power BI makes it easy to share those same models and data to the entire organisation via dashboards and apps. The Microsoft stack alignment enables a seamless flow between data, analysis, and organisational sharing. For organisations invested heavily in Microsoft technology, Power BI is a natural fit to extend that analytics foundation. A key strength of Oracle Analytics Cloud is its semantic model that abstracts the complexity of the underlying data and technology stack from end users. Business analysts can access and analyse data without needing to understand the physical tables and relationships. OAC also enables strong data governance with centralised security rules, data logic definitions, and stewardship processes applied consistently across the semantic models. This top-down approach ensures quality and trust in the data while still empowering decentralised analytics. How They Can Work Together There is Power BI supported connectivity to Oracle Analytics that gives Power BI users access to Oracle Analytics content. Oracle Analytics provides an easily configured connector that enables Power BI Desktop access to the Oracle Analytics semantic model. More details on how to set it up can be found here. It should be noted that there are a number of limitations:
Conclusion Power BI and Oracle Analytics Cloud both offer compelling capabilities for data visualisation, reporting and analytics. Rather than viewing them as competing tools, organisations should consider how they can work together in a hybrid analytics environment. The key is to play to the strengths of each platform:
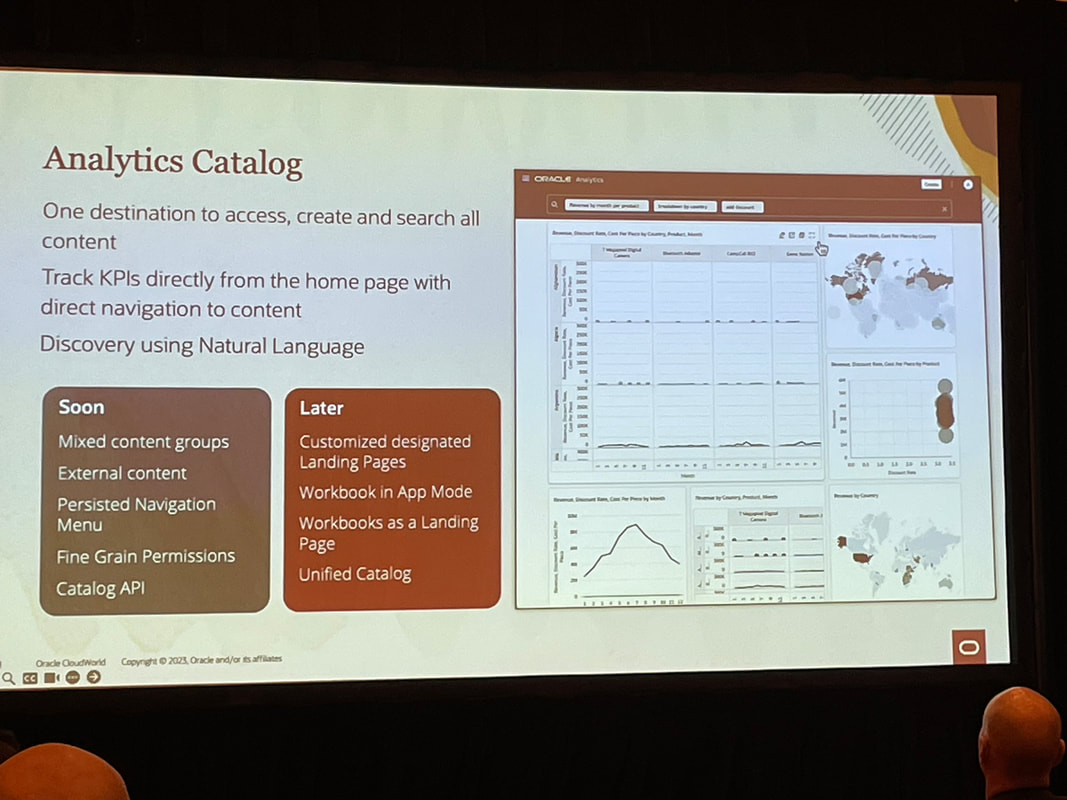
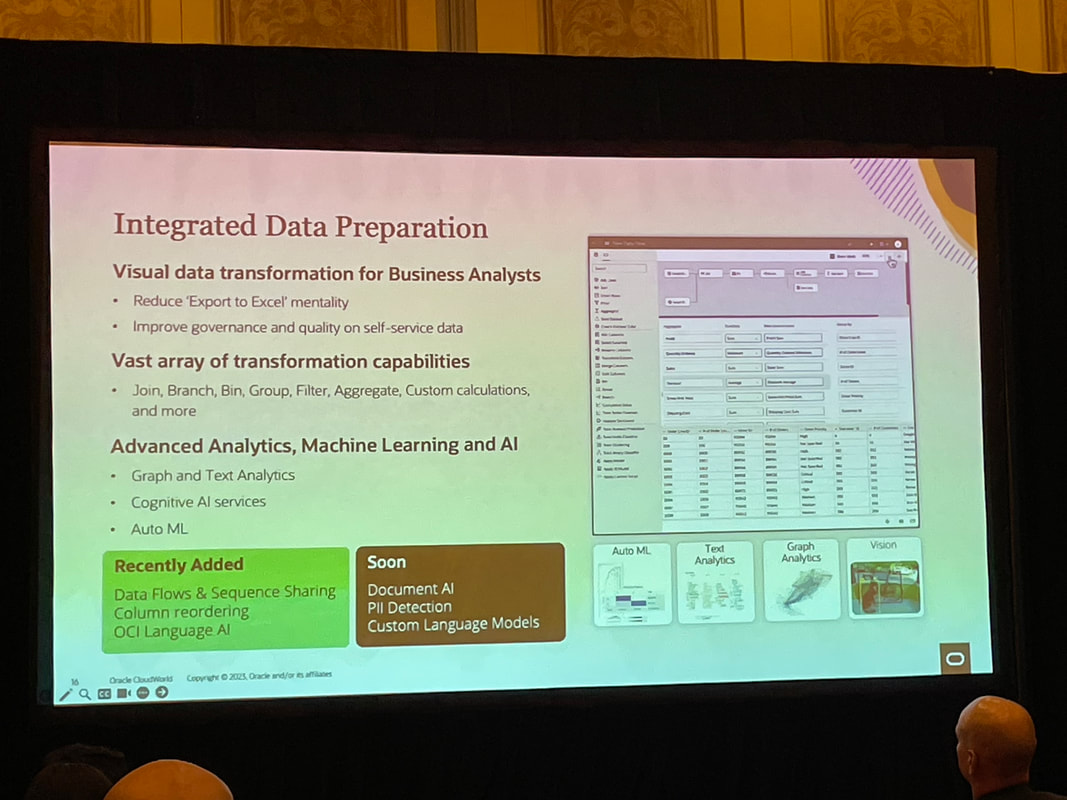
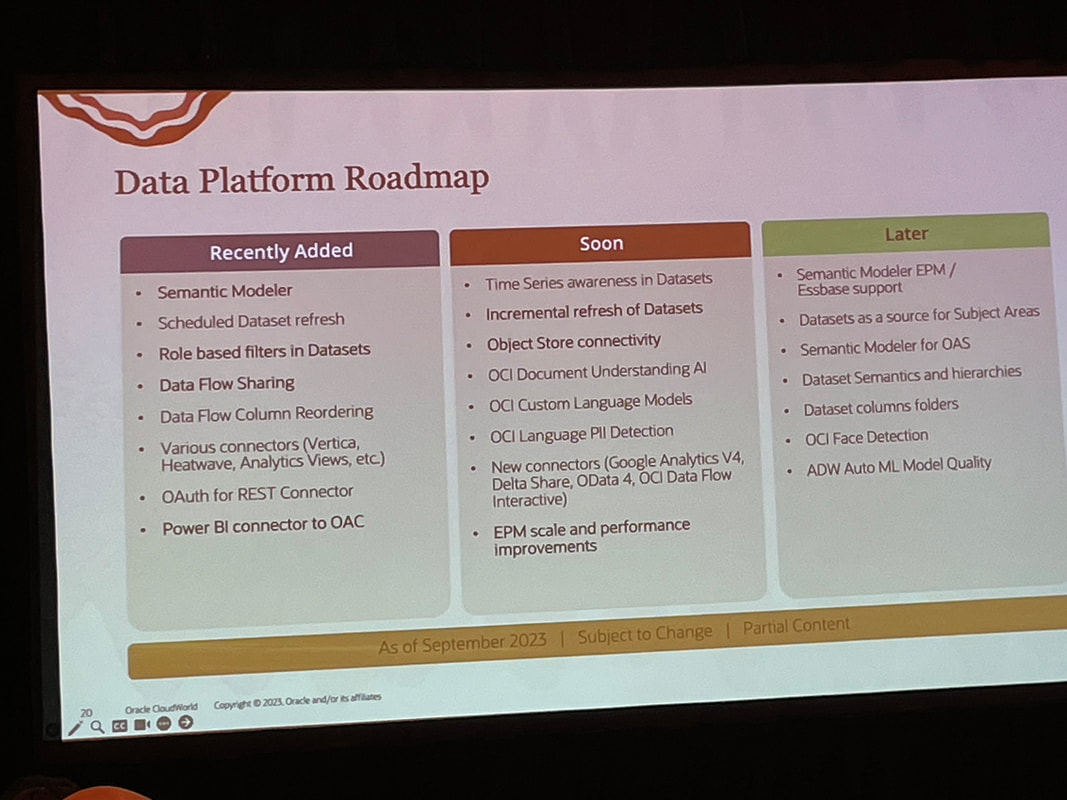
By taking a hybrid approach, both business users and data experts can win with the analytics capabilities they need. Rather than analytics chaos, a "best of both worlds" environment can emerge. Organisations can optimise their analytics investments and empower people with the right insights at the right time.  Unless you’ve been living under a rock, you won’t be surprised to know that the main theme of CloudWorld this year at Las Vegas was generative AI. Almost every Oracle product from databases, to Fusion applications, to OCI, APEX and Analytics to name but a few announced generative AI functionality at the recently concluded Oracle CloudWorld 2023 in Las Vegas that I attended. My journey from the U.K. to Las Vegas was "eventful" and could be a separate blog in its own right! Generative AI differs from traditional AI in that it creates new data similar to its training data, rather than just analysing data and making predictions. With advances in large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3, there is huge potential for generative AI to transform many industries including how analytics is consumed. Keynotes In his keynote, Larry Ellison discussed how Oracle is well-positioned as a cloud provider to power the infrastructure and services needed for the next generation of generative AI applications. Foundational machine learning models from OpenAI, XAI, Anthropic and Cohere can provide the backbone for cutting-edge LLMs. As Safra Catz emphasised in her keynote, Oracle's focus remains on putting customer success at the heart of everything. New offerings like Uber Direct, a last-mile retail delivery solution developed by Uber in partnership with Oracle, exemplify Oracle's drive to enable digital transformation for organisations. Ellison started off with pointing out how generative AI is “the most important technology ever” and how new applications will no longer be developed in Java as these will all be built with code created by generative AI. He highlighted how Oracle's APEX low-code platform is evolving to empower no-code development as well. Solutions like Autonomous Database for Fusion and NetSuite will further automate cloud services. And Oracle aims to support open, connected multi-cloud through seamless interoperability between platforms. He also announced a new Oracle Cloud Data Intelligence Platform which is at a high level, a combination of Oracle Analytics and Generative AI. It will be interesting to find out more about this new platform when more information becomes available. In the words of Emerson COO Ram Krishnan in his discussion with Safra Catz, "Vision without execution is hallucination." Oracle's vision for cloud-enabled generative AI shows promising signs of execution. Analytics I attended several Oracle Analytics sessions and I’ll attempt to summarise what I gathered from these sessions below. Contextual Insights is a new feature that was demonstrated in Gabby Rubin’s Oracle Analytics Roadmap and Strategy session. It was also shown during Philippe Lion’s Analytics and OCI AI session. This new feature will be available to consumers unlike features like Auto Insights that are only available to Authors. The new feature allows users to select a specific value in a visualisation and the automated Machine Learning generates additional visualisations based around the selected visualisation value in a similar fashion to the auto insights feature but it is within context of the selected visualisation value. There are also plans to consolidate access to catalog content as well as to make external content accessible. Another feather in the pipeline is the ability to set fine grain permissions on catalog objects rather than the current one size fits all. In Gabby’s roadmap session, which is always great as it gives you information on upcoming features that can be expected to rollout soon (there’s always a caveat about what “soon” means). One such feature mentioned was the flexibility available when an OAC instance is provisioned. This has recently been increased to 8 sizes that can now be selected. The long-term plan is to give customers complete shape flexibility when Oracle Analytics Cloud is being provisioned. Another point made that I was admittedly unaware of is that Oracle Analytics Server and Oracle Analytics Cloud only share a very small amount of source code. This is the main reason why there is a significant difference in the Oracle Analytics Cloud and Oracle Analytics Server release cycles; every 2 months for Oracle Analytics Cloud and annually for Oracle Analytics Server. In the integrated data preparation area, PII (Personally Identifiable Information) is coming soon. My take on this is that this will be another recommendation on the data preparation step. The web based semantic modeller support for EPM & Essbase data sources is also something eagerly awaited and, on the roadmap, marked as “later”. The information from this strategy update is publicly available and can be found here. Catalog Manager It was recently announced that the Catalog Manager GUI will be desupported from the January 2024 Oracle Analytics Cloud update. The command line interface will still be available to use from that point. The January 2024 update will not ship with the Catalog Manager client tool however, you’ll still be able to use existing installations of the Catalog Manager client if needed. The strategic plan is for the Catalog Manager client tool to be completely replaced by a web-based Catalog Manager. There are also OAC catalog APIs in the works as well. T.K. Anand had a session which I couldn’t attend that provided some more context and information about Larry Ellison’s announcement about Oracle Cloud Data Intelligence Platform. I think that this is going to bring Oracle Analytics and the Fusion Analytics platform under one umbrella in conjunction with generative AI. If this is the case, then it will simplify the Oracle Analytics offering doing away with all the confusion around which of the products are best suited to specific customers. I’ll be keeping an eye on developments on this. My PresentationI presented at CloudWorld for the first time, and it was an interesting experience. Tim German, the Version 1 US EPM Practice Head was a co-presenter. The topic we covered was “from data to insights with Oracle Analytics”. We had a really great turnout with standing room only and about 100 people in attendance, we had to cram a lot of content into a 20-minute theatre session to demonstrate the capability of Oracle Analytics to enable users to gain insights from their data assets. The key takeaways of the session were that Oracle Analytics: • allows users to connect to a variety of data sources. • users can easily visualise and analyse data. • built-in machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities • tools for data preparation. • collaboration and sharing features. CloudWorld has been a positive experience, and I had the opportunity to meet a lot of people in person for the first time that I’ve only seen on Zoom and Teams calls! As an Oracle ACE Pro, I enjoyed the Oracle ACE events which were good fun where there were over 100 Oracle ACEs in attendance at the ACE dinner! I also got to meet some of the Version1 Oracle ACEs in person too. I just hope that my luggage won’t be overweight on my way home with all the swag that I picked up!
In the dynamic landscape of data analytics, businesses are in search of a comprehensive solution that seamlessly integrates data governance, self-service analytics, augmented insights, and robust reporting. Oracle Analytics emerges as a unified platform that stands out amidst the competition. Let's draw a comparison with other leading tools – Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik – and delve into Oracle's key differentiator: the Semantic Model, and how it empowers cross-platform compatibility. Comparing Solutions: In a landscape where specialised tools often excel in specific areas; some examples stand out:
In contrast, Oracle Analytics emerges as the bridge that seamlessly connects and combines these functionalities, underpinned by the powerful and unique Semantic Model. Unlike other vendor solutions that focus on one specific area of Analytics, Oracle Analytics unites governed analytics, self-service analytics, and augmented analytics within a single, cohesive platform.
The Power of the Oracle Analytics Semantic Model:
Connecting with Other Tools: Oracle Analytics' Semantic Model acts as a conduit between ecosystems. Tools from different vendors can access the model via APIs or connectors. This integration allows businesses to leverage the model's standard data representation across various analytics solutions. Unlocking Seamless Integration: Imagine utilising Tableau's immersive visualisations alongside Oracle Analytics' robust data governance, all powered by insights from Power BI's AI-driven engine. Oracle's Semantic Model paves the way for this harmonious integration. By providing a shared understanding of data, the model fosters interoperability. Businesses can confidently combine strengths from multiple analytics tools to derive deeper, actionable insights. Empowering Diverse Analytics Personas with Oracle Analytics:
The goal of Oracle Analytics is to empower all personas across organisations to make data-driven decisions through easy, intelligent, and connected analytics experiences. The versatility caters to both highly technical and business casual users. A Path Forward: Embrace Unity with Oracle Analytics:
Summary: In this blog, we've explored the wide spectrum of data analytics and uncovered Oracle Analytics as a standout solution that unifies data governance, self-service analytics, and augmented analytics. Contrasting with other tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik, Oracle Analytics emerges as a singular platform that seamlessly blends these functionalities, promoting collaboration and compatibility. The Semantic Model empowers users with simplified data access, consistent results, and unprecedented interoperability across various vendor ecosystems. By embracing Oracle Analytics, businesses can harmoniously bridge the gaps between governed analytics, self-service exploration, and AI-driven insights, driving data-driven strategies into new dimensions. |
AuthorA bit about me. I am an Oracle ACE Pro, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure 2023 Enterprise Analytics Professional, Oracle Cloud Fusion Analytics Warehouse 2023 Certified Implementation Professional, Oracle Cloud Platform Enterprise Analytics 2022 Certified Professional, Oracle Cloud Platform Enterprise Analytics 2019 Certified Associate and a certified OBIEE 11g implementation specialist. Archives
May 2024
Categories |
























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

